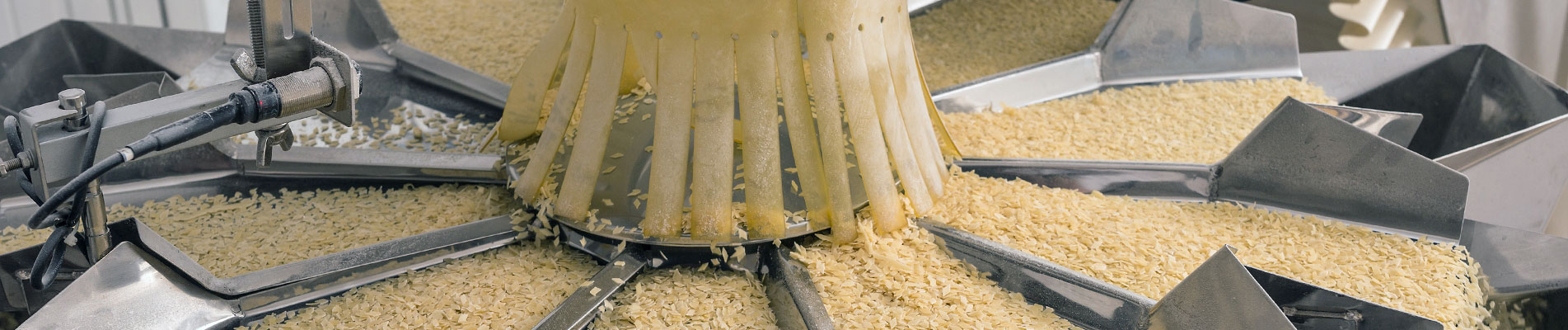
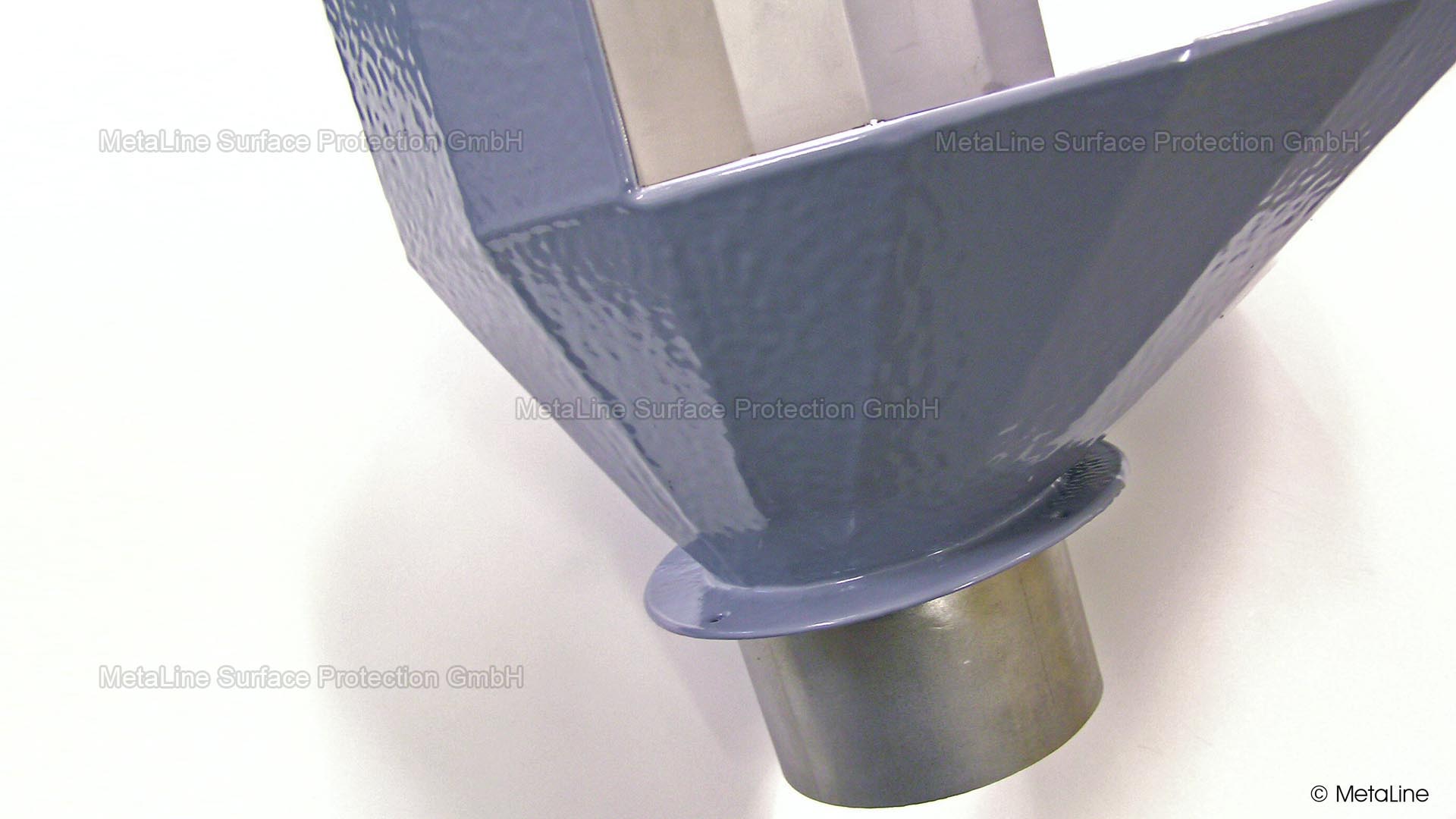
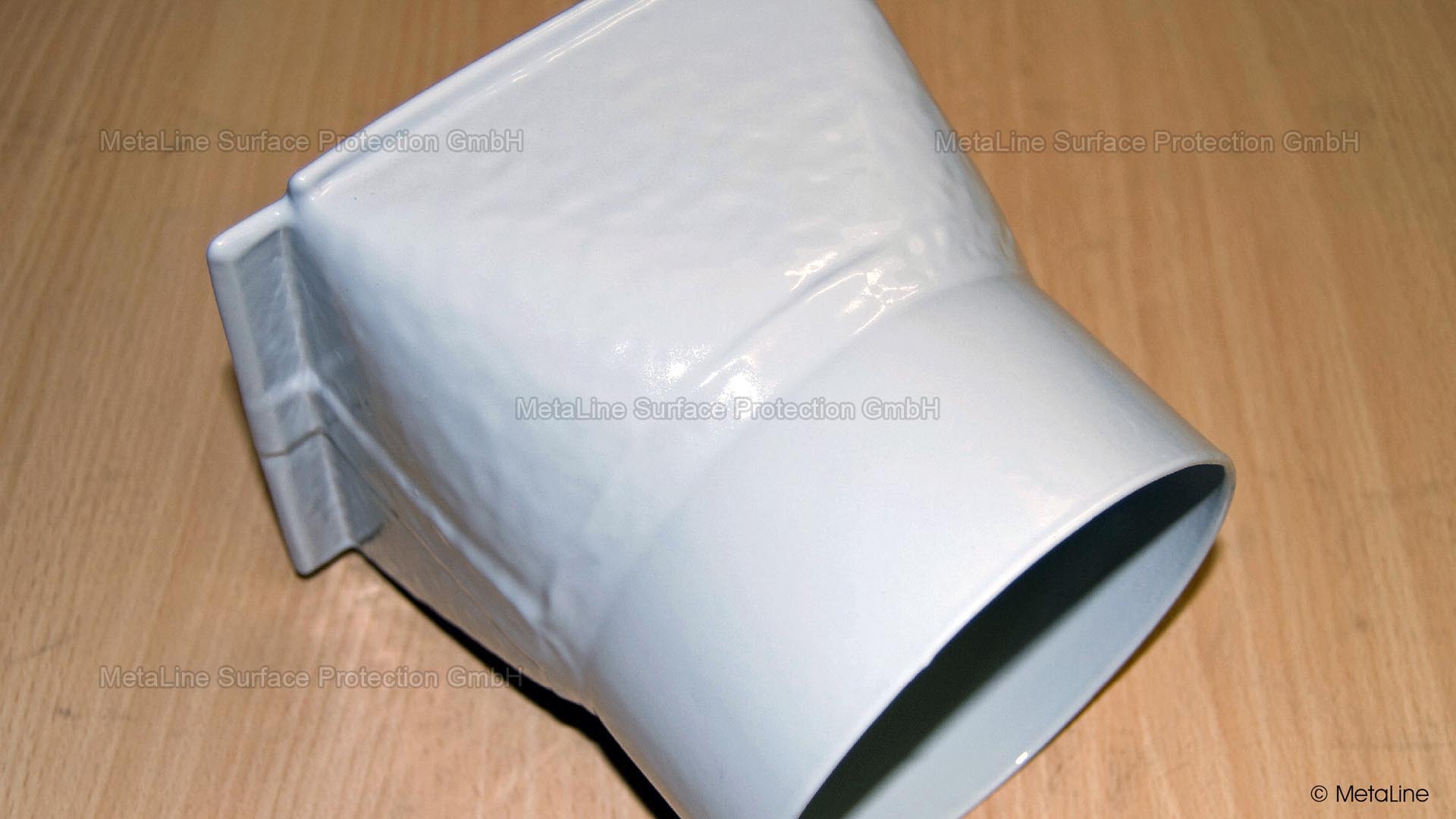
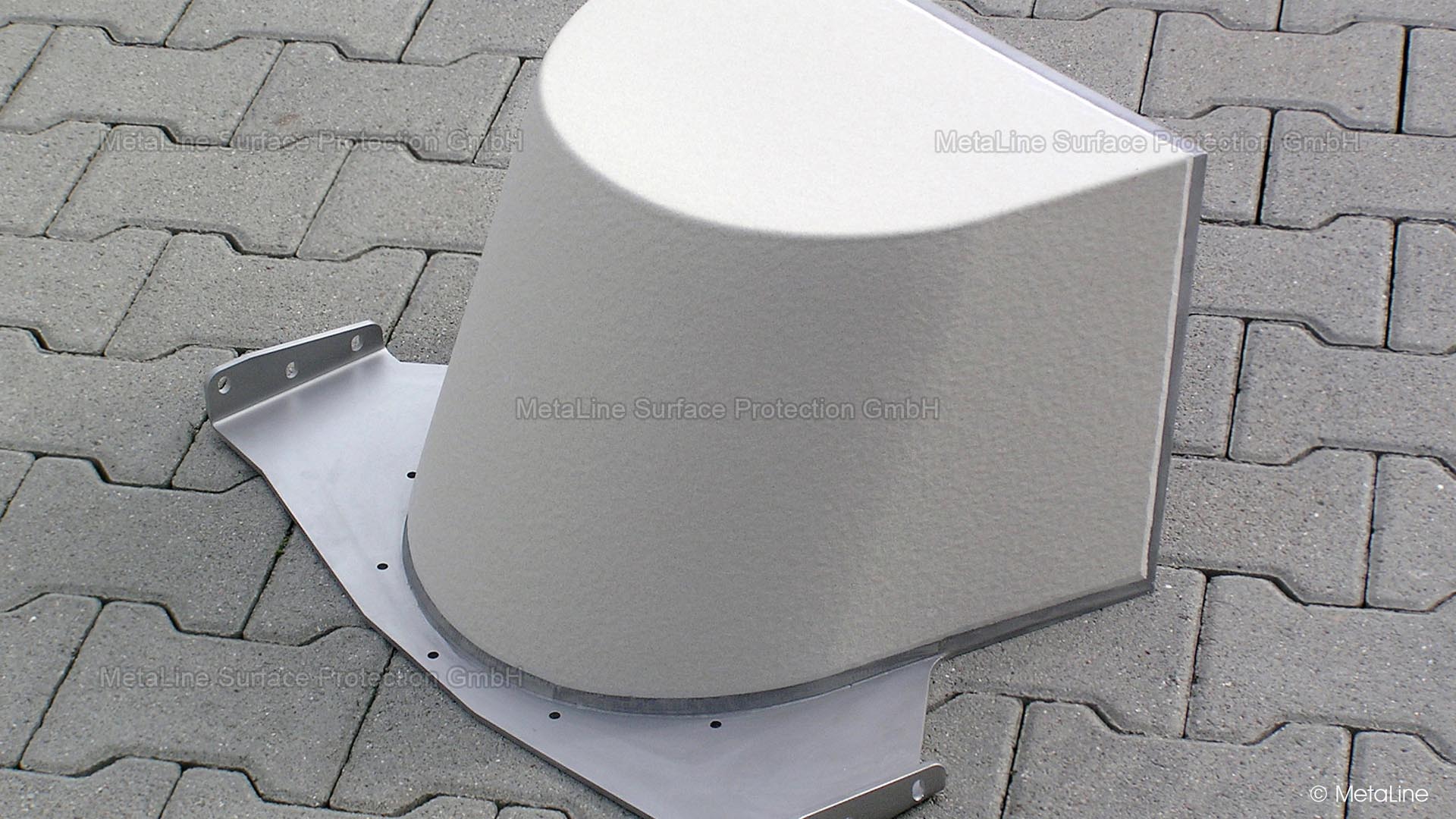
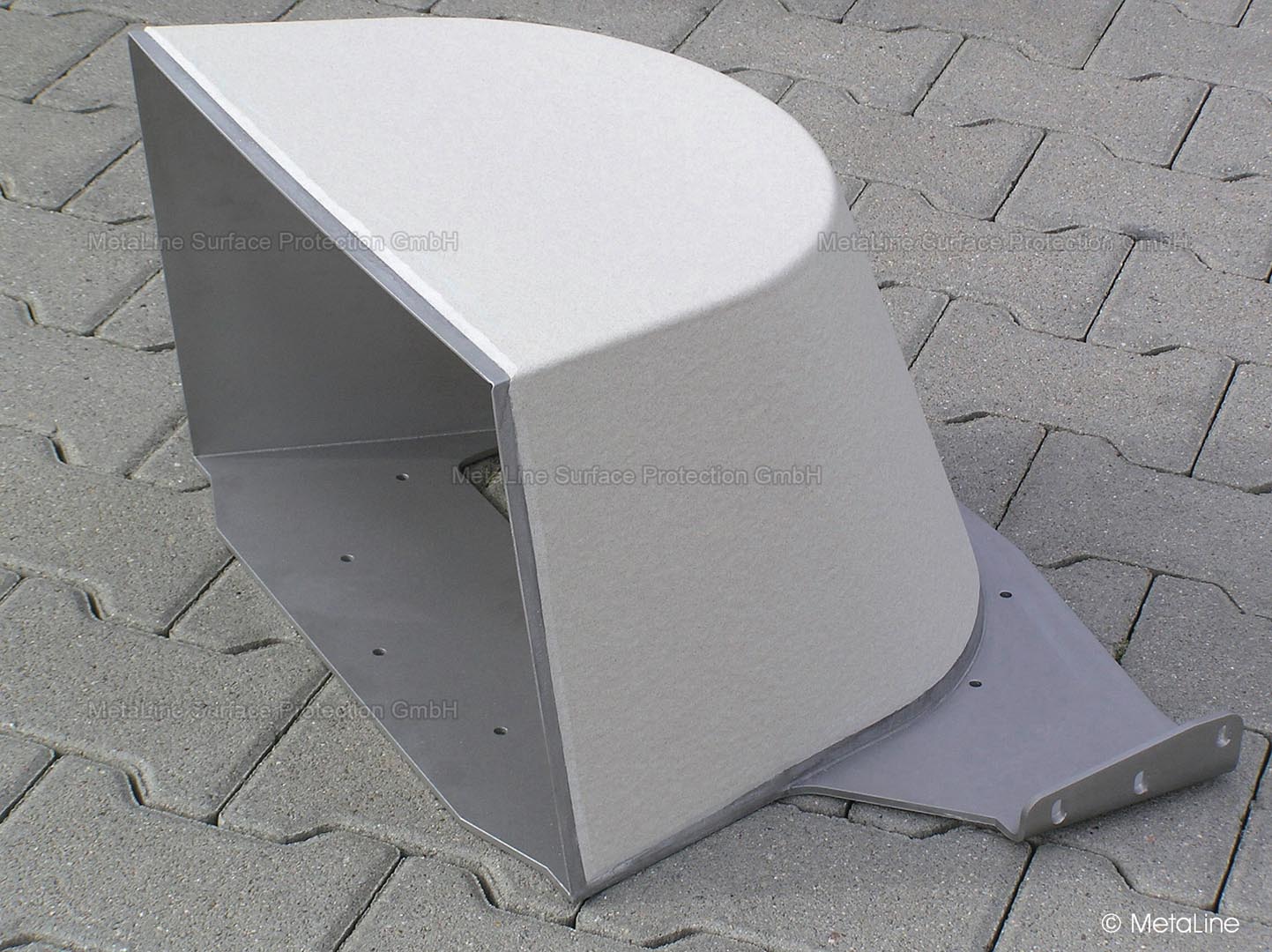
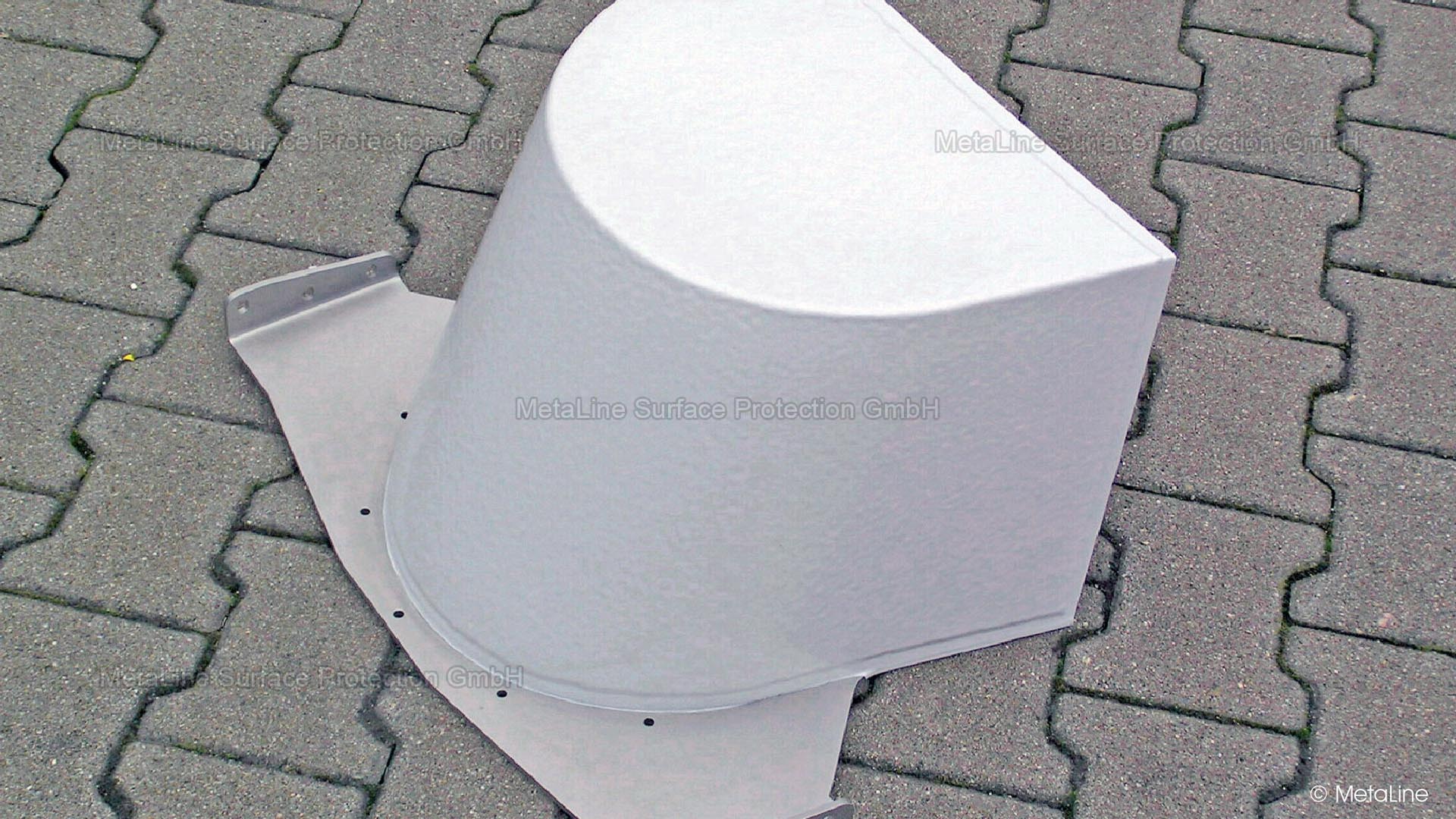
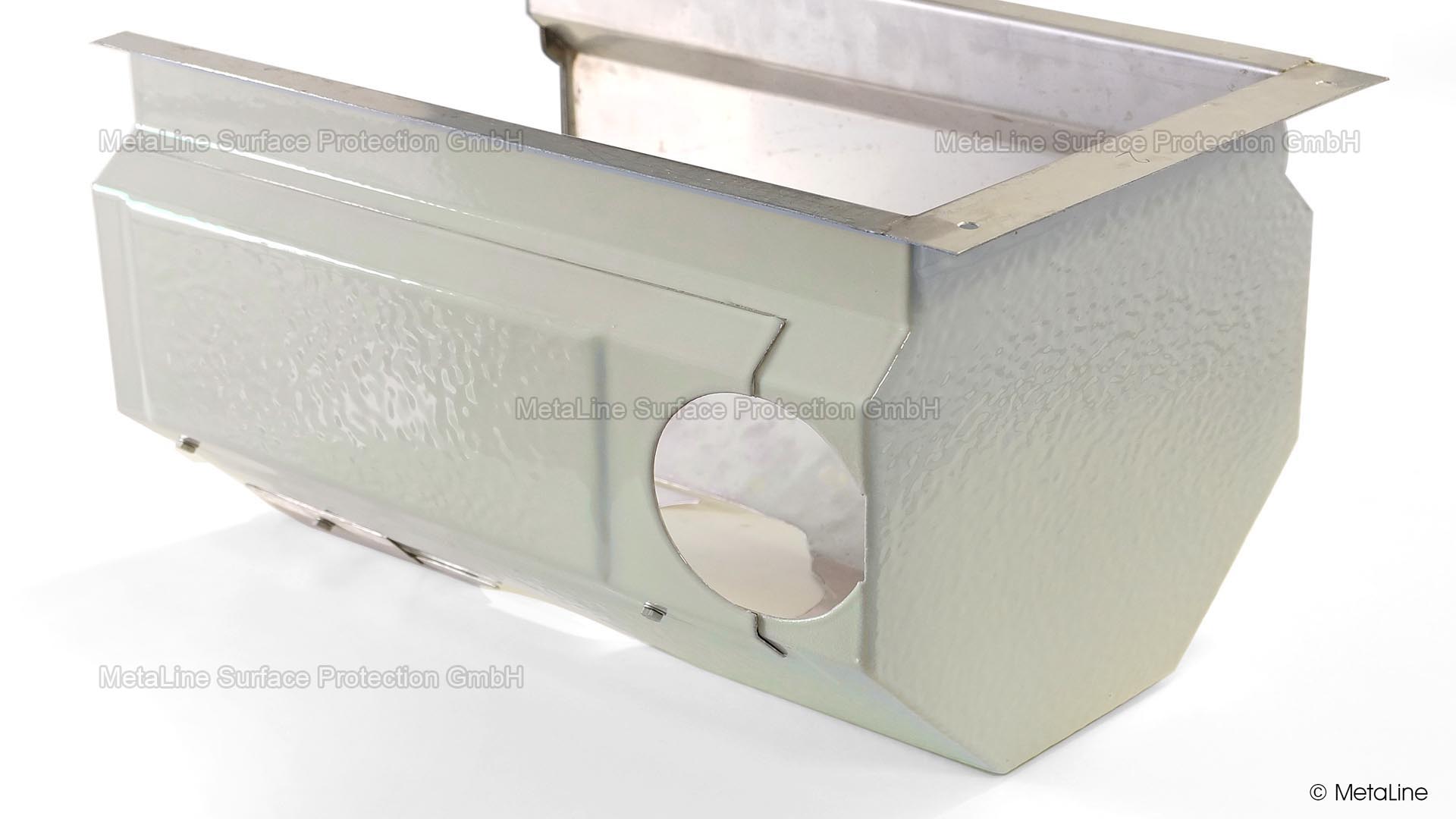
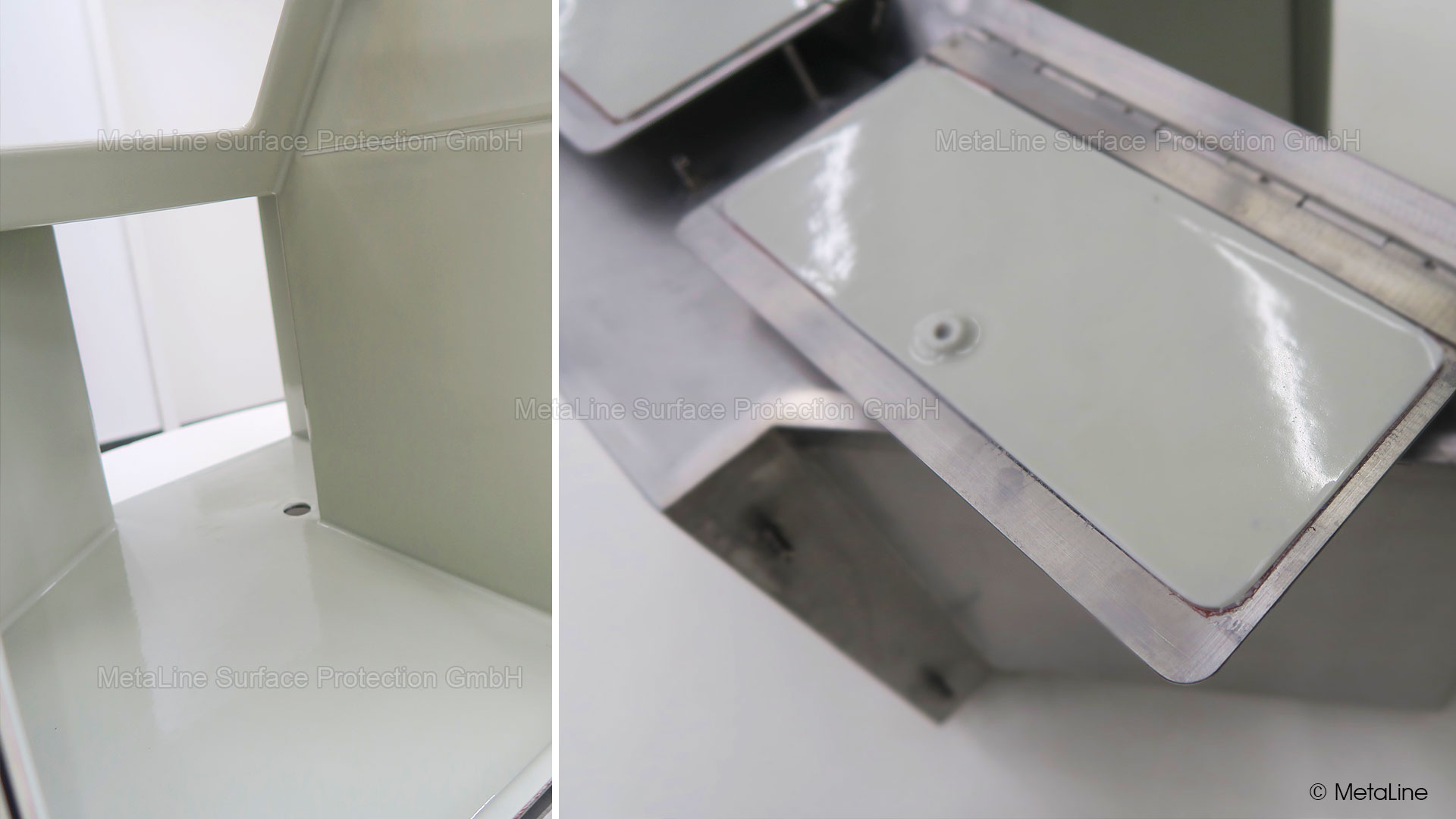
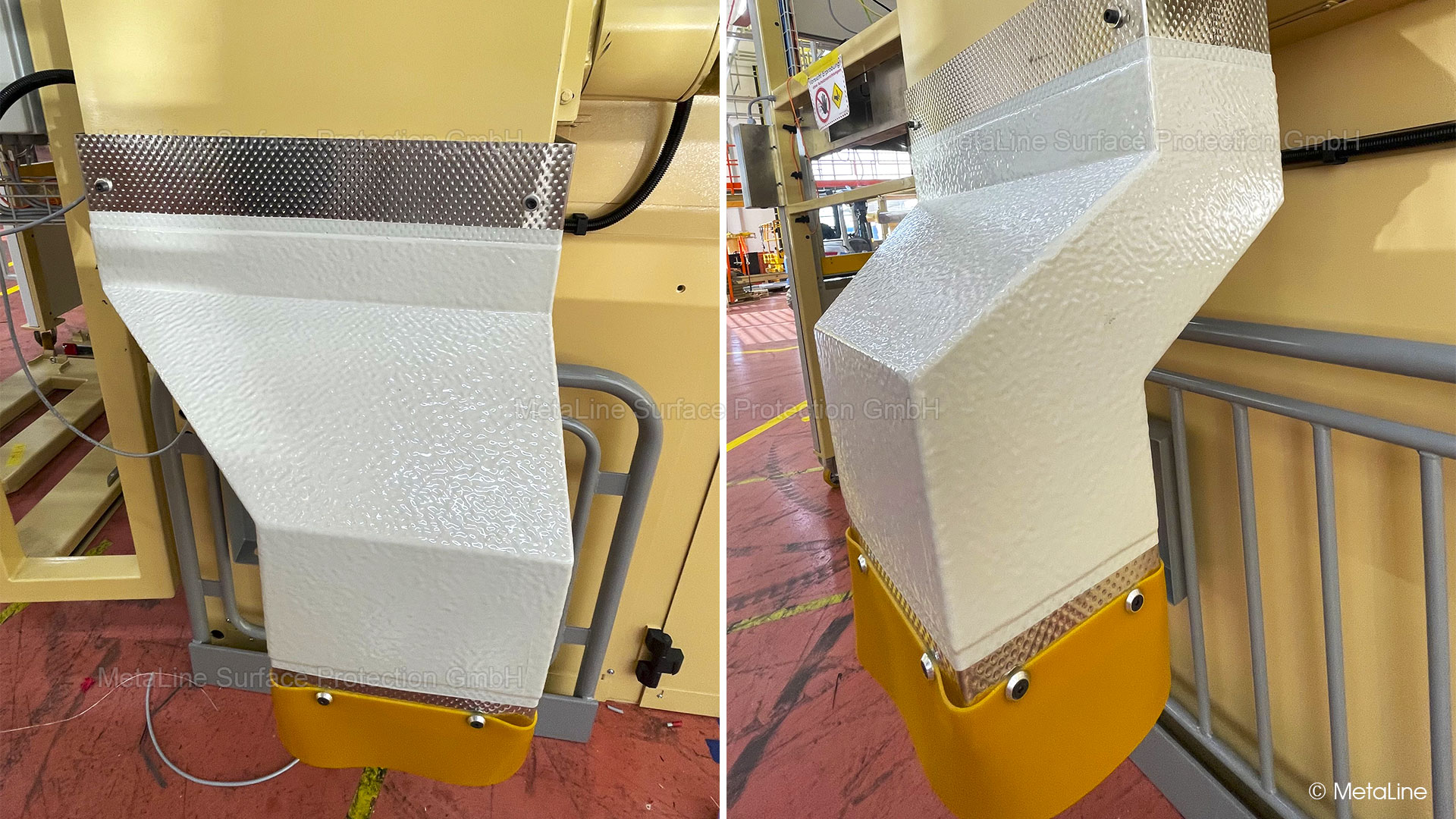
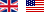
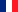
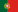
Body sound reduction - this chute in a food packaging machine has been noise reduced with MetaLine 440 and a top coat of MetaLine 795. The smooth and non-porous surface structure offers perfect cleaning capabilities and an undisturbed long-time function
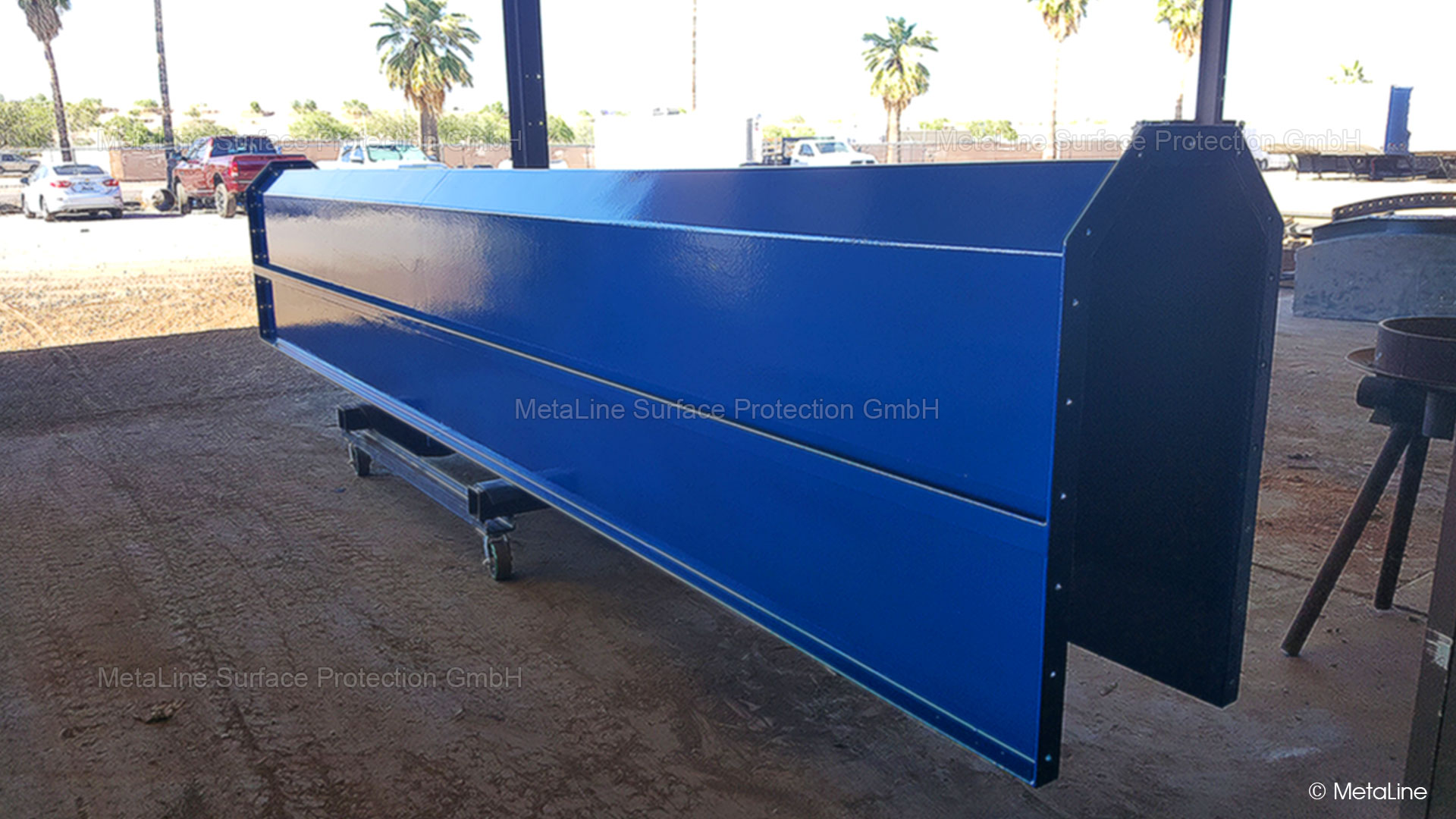
Sound deadening coating - this metalic connector in a pneumatic feeding system has lost all its disturbing noise character after the professional treatment with MetaLine 440
Noise absorbing coating - metalic feeding unit of an assembly unit. A 3 mm thick coat of MetaLine 440 optimizes the body sound properties. Without any resonance after treatment - like a FRP structure
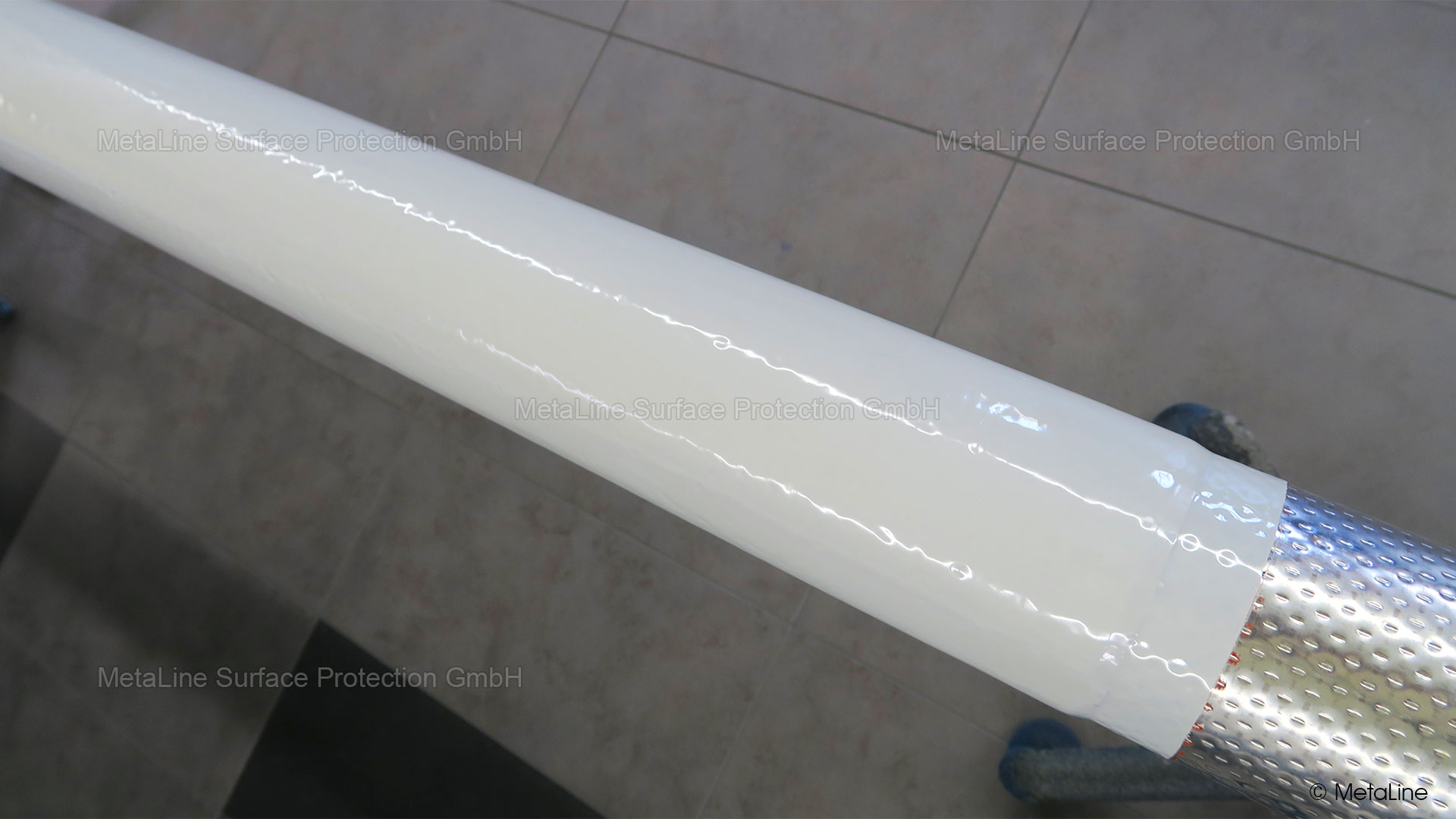
Noise reducing treatment - the MetaLine 440 sound isolated part can be overpainted with most varnishes. The sealing of the porous surface structure is essential in order to avoid moisture absorption
Sound reducing coating - a treatment with MetaLine 440 can be finalized with a top coat of MetaLine's FDA approved (pharmaceutical) Series 500 or 700 coatings
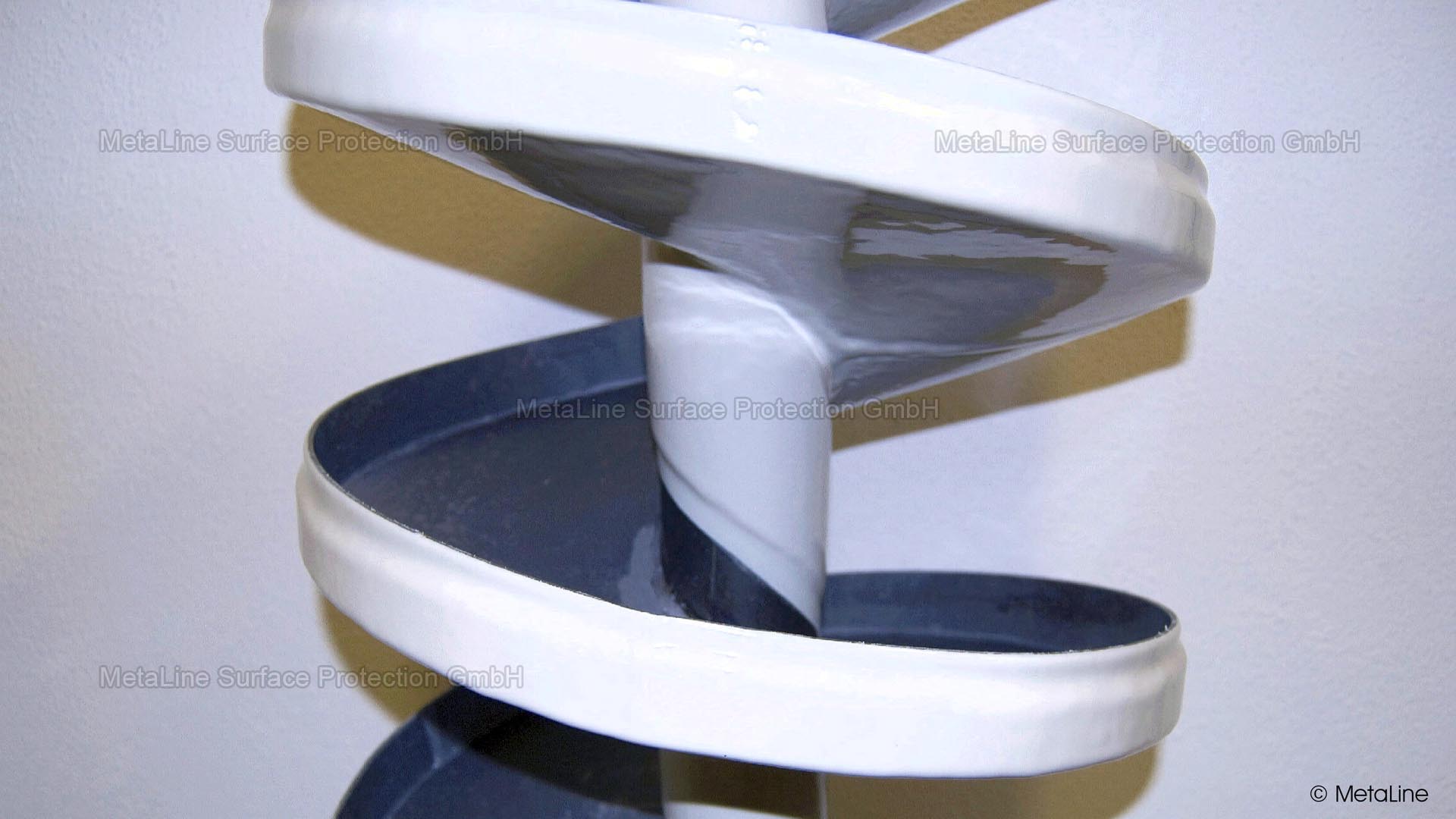
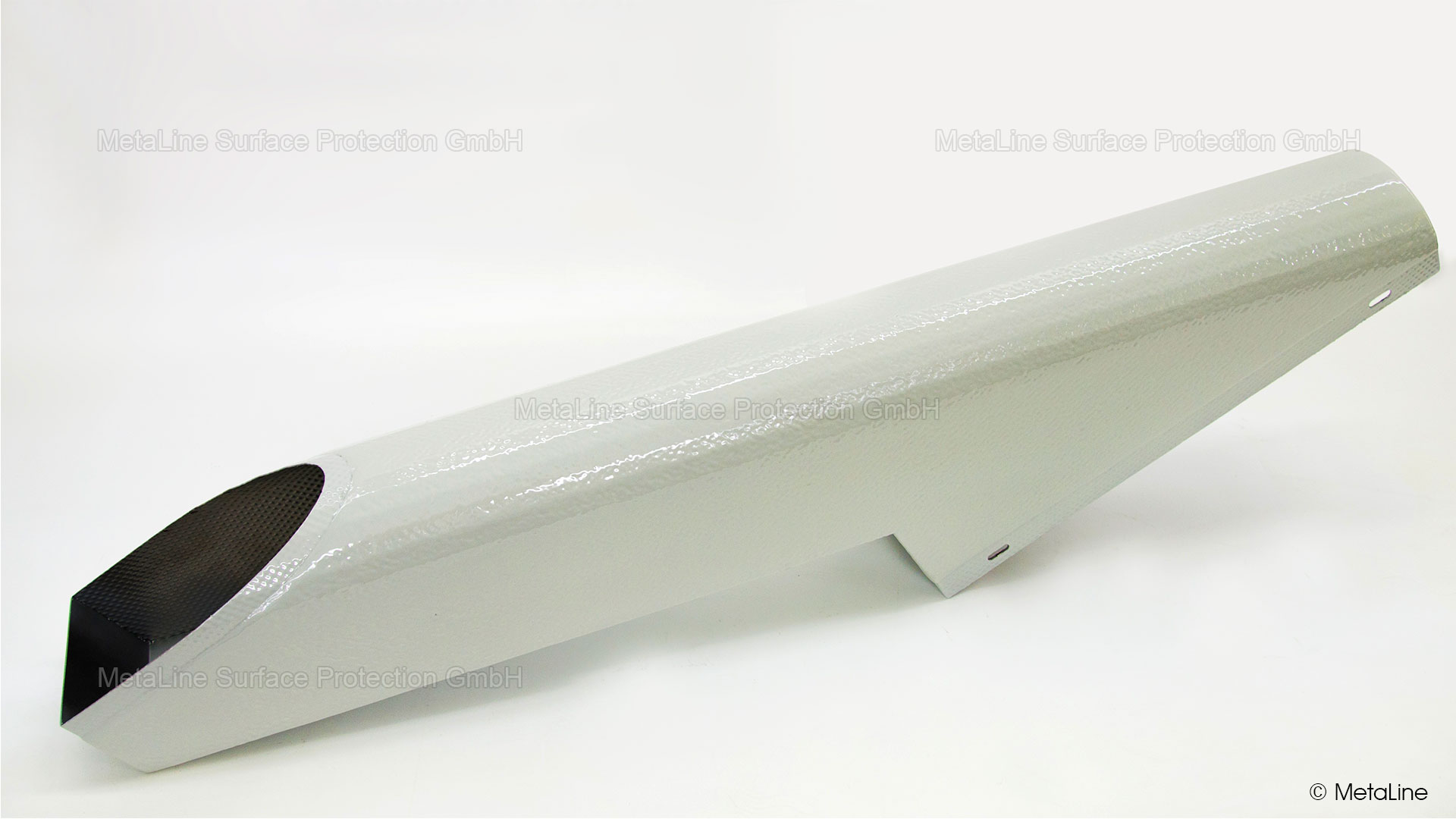
Noise minimizing coating - after treating this sprial chute a significant drop of 12 dB(A) in noise could be realized. This without disturbing the inner sliding characteristics of the chute
Sound reduction - this term is not technically correct. Our structure-borne sound-reducing coating prevents sound from being generated in the first place. Sound that is already spreading in the air can no longer be neutralised with a coating. In other words, MetaLine "gets to the root of the problem"!
Noise encapsulation - Reducing structure-borne noise with MetaLine 440 does not have to be a full-surface application. Depending on the material and the component geometry, a partial coating is sufficient - money saved!
Droning reduction - droning reduction with MetaLine 440 is visually dull, somewhat uneven and not attractive. MetaLine 440 should be imperatively sealed by painting or MetaLine Series 500/700 coating in case of moisture, liquid contact, presence of organic substances and similar!
Noise inhibition - it's pure physics! The design of the coating has an influence on its effectiveness. MetaLine is a specialist in textures of coatings to achieve the best possible results. There is no substitute for experience!
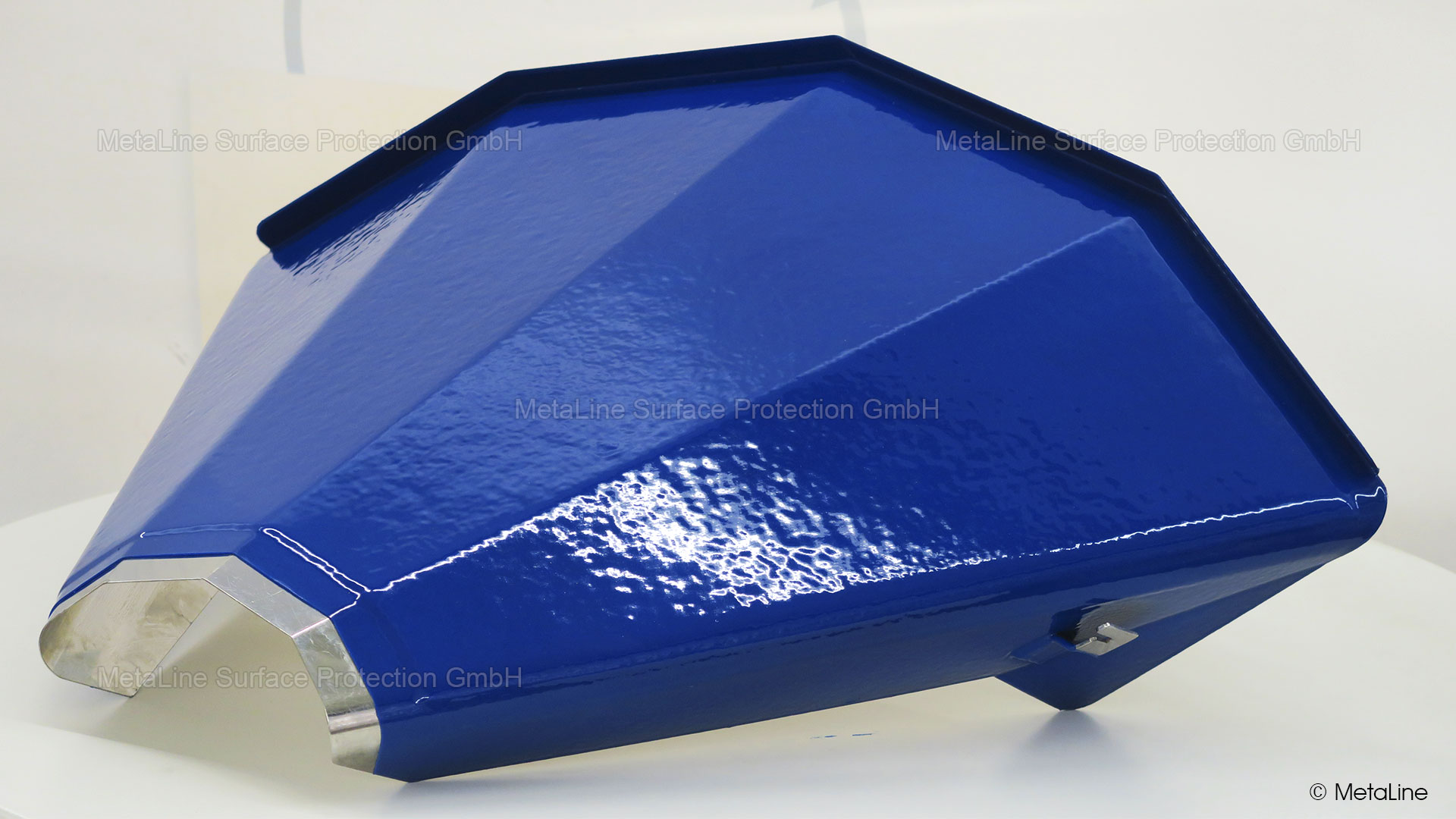
Sound insulation - can be so beautiful! MetaLine coatings can satisfy visual needs and improve functionality. Design meets optics!
Noise control - quietness in the workplace is not a luxury, but a health need. MetaLine 440 reduces all high frequencies and eliminates reverberant resonance - a perfect start!
Drone protection - in the food and pharmaceutical sectors. With its FDA conformity, MetaLine is a safe bank in hygiene applications. Not only because of the certification - but because nothing can flake off from a rubber! Unlike rigid paint systems!
Noise emission - in this case triggered by metallic fittings. A constant banging and clanking. Watch the MetaLine 440 video and you will know how quiet the machine has become after our treatment!